Authors:
Khushi Jaiswal、Ievgeniia Kuzminykh、Sanjay Modgil
Paper:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.10788
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming industries and creating a significant demand for skilled professionals. According to LinkedIn News (2023), roles such as Machine Learning Engineers have seen a 74% increase in demand over the past six years. Similarly, LinkedIn News (2024) identified Artificial Intelligence Engineers as one of the top 10 careers in the UK. Despite this growing demand, there is a notable skills gap between what universities teach and what industries require. This study aims to investigate this gap by comparing the skills taught in AI courses at UK universities with those demanded by the industry.
Related Work
Previous Studies on Skills Requirements
Several studies have explored the skills required in the AI and Machine Learning (ML) sectors. Verma, Lamsal, and Verma (2022) analyzed job advertisements in the US market, revealing a significant demand for AI and ML professionals. Their methodology involved web scraping job descriptions from indeed.com and using n-gram techniques for content analysis. Similarly, Attwood and Williams (2023) investigated the skills gap in the cybersecurity industry, using TF-IDF representations to map job descriptions to the Cyber Security Body of Knowledge (CyBOK).
Data Collection Methods
Han and Anderson (2021) compared various data collection methods, including web scraping, APIs, surveys, and simulation studies. They concluded that web scraping is cost-effective and provides large-scale, real-time data. This method has been widely used in previous studies, including those by Verma, Lamsal, and Verma (2022), and Attwood and Williams (2023).
Skills Gap in AI Education
Sarin (2019) identified a disparity between the skills perceived as important by students and those valued by employers. The study involved collecting primary data from students and HR executives, revealing that students often focus on quantitative topics while employers value communication skills and domain knowledge.
Research Methodology
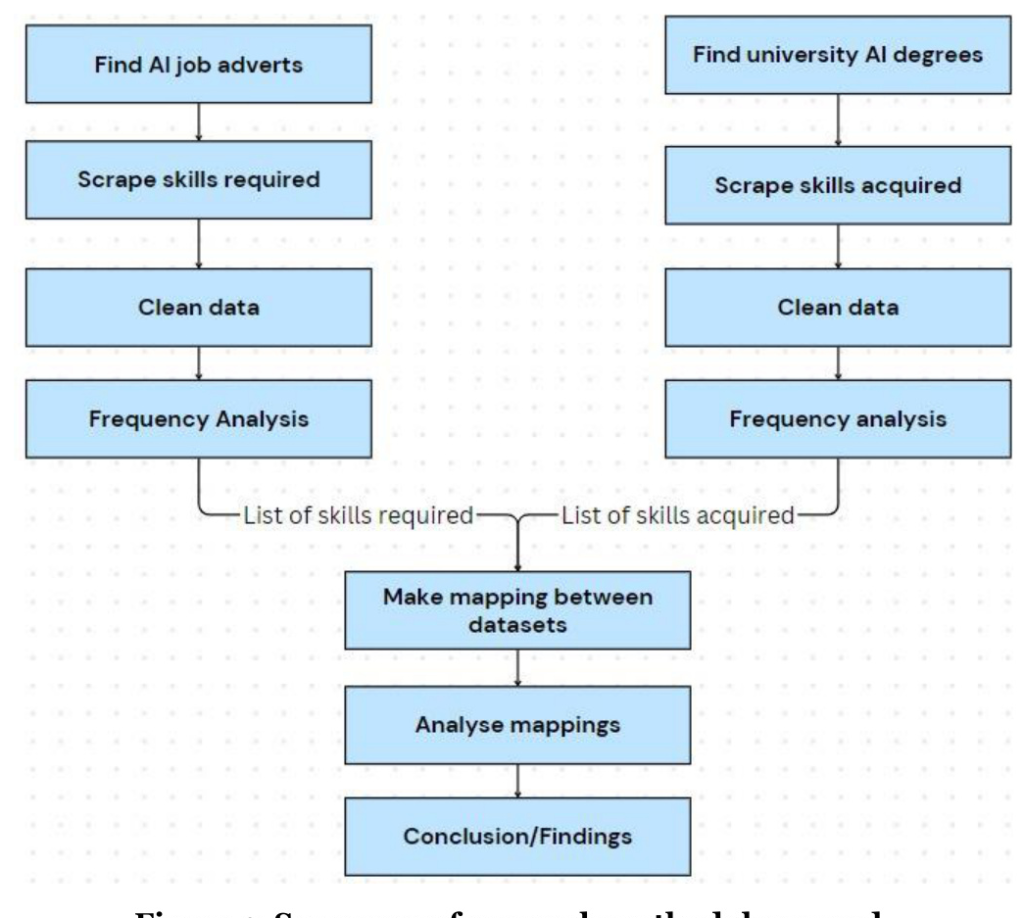
Data Collection
The study used LinkedIn as the primary job advertisement platform due to its detailed job descriptions and filtering options. A Chrome extension called Clay was used to scrape data from LinkedIn, collecting information on required skills from 158 AI-related job adverts. For university curricula, data was collected from the websites of 30 top UK universities offering AI courses.
Data Processing
Both datasets were cleaned using the Python Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) to remove stop words, symbols, numbers, and whitespaces. The text was then split into individual words and converted to lowercase. Word phrases of lengths from 1 to 5 were extracted to identify the most common skills.
Data Analysis
A frequency analysis was conducted on both datasets, collecting the top 400 most commonly occurring phrases for each of the 5 different lengths of phrases. The skills were then categorized into 12 distinct categories using a Naive Bayes classifier, which showed an average precision of 87% and an average F1-score of 82%.
Experimental Design
Job Adverts Analysis
The geographical distribution of AI-related jobs in the UK was analyzed, revealing that most jobs are concentrated in London. The study also found that 9.5% of jobs offered remote working options. Salary ranges varied widely, with the highest salaries typically found in London.
University Degrees Analysis
The study analyzed AI courses offered by 30 top UK universities. It was found that 61 out of 166 UK universities offer undergraduate AI courses, with 79 offering MSc degrees in AI. The popularity of online programs is rising, with around 10% of AI degrees being delivered remotely.
Frequency and Mapping Analysis
The frequency analysis showed that the most commonly sought and taught skills are related to machine learning, programming, and software development. The mapping analysis revealed a skills gap in areas such as Data Science and Analytics, and Maths and Statistics.
Results and Analysis
Key Findings
- Strong Technical Skills Dominance: Both university degrees and AI jobs emphasize programming and machine learning skills.
- Increased Demand for Data Science: Data Science and Analytics skills are more in demand in AI jobs compared to university curricula.
- Business and Management Skills: These skills are more sought after in AI jobs than in university courses.
- Emphasis on Soft Skills: Both datasets emphasize the importance of soft skills.
- Maths and Statistics: These skills are highly demanded by job adverts but are not as prominently taught in universities.
- Ethics Recognition: Both sets recognize the importance of ethics in AI.
Discussion
The study identified 35 skills organized into 12 categories. The most in-demand skills in the UK job market are programming and machine learning, similar to findings in the US. However, there is less demand for big data skills and maths & statistics in the UK compared to the US. The study also found that recruiters prefer well-rounded candidates with strong analytical skills and good communication abilities.
Overall Conclusion
The study aimed to identify the skills gap between AI jobs and university AI degrees in the UK. The findings showed that while there is a good balance in most technical skills, there is a significant gap in Data Science and Analytics, and Maths and Statistics. Universities need to focus more on practical applications of these skills and incorporate more business and management training. Additionally, both universities and industries should place more emphasis on ethics-related skills.
The insights from this study can help universities update their curricula to better align with industry requirements, ultimately reducing the skills gap in the AI sector.