Authors:
Lei Zhang、Jin Pan、Jacob Gettig、Steve Oney、Anhong Guo
Paper:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.09382
Introduction
As Virtual Reality (VR) continues to gain traction in various fields such as education, gaming, and spatial design, the need for effective tools to create high-quality 3D scenes becomes increasingly important. Immersive authoring allows users to create and evaluate 3D scenes directly within a virtual environment, leveraging their spatial capabilities. However, the manual creation of 3D layouts can be tedious and time-consuming, limiting the exploration of diverse ideas. Recent advances in generative AI models offer a promising solution by enabling the automatic creation of realistic 3D layouts. This study introduces VRCopilot, a mixed-initiative system that integrates pre-trained generative AI models into immersive authoring workflows to facilitate human-AI co-creation in VR.
Related Work
Generative Models for 3D Scenes
The demand for automatically generating 3D scenes is high in domains such as gaming, AR & VR, architecture, and interior design. Prior research in 3D scene synthesis has explored generating new 3D scenes via various inputs, including images, text, or room shapes. Data-driven approaches, leveraging large 3D object datasets, have shown promising results in generating realistic 3D layouts. VRCopilot contributes to this field by integrating state-of-the-art generative AI models into immersive authoring, exploring ways of co-creating with these models in VR.
Creativity Support via Steering Generative Models
Human-AI co-creation has been explored in domains such as drawing, creative writing, video game content creation, and music composition. However, there has been relatively little research on designing interactions with generative models for co-creation in immersive environments. VRCopilot addresses this gap by investigating how users express their preferences to generative AI through multimodal specification and intermediate representations in VR.
Interaction Techniques in Immersive Environments
Prior interaction techniques in immersive environments, such as multimodal interaction and spatial interaction, have inspired the design of VRCopilot. The system demonstrates how multimodal interaction can be used for specifying objects to generative AI in the immersive authoring process. Additionally, the concept of World in Miniature (WIM) is utilized to enable users to design and edit multiple variations of 3D layouts.
Research Methodology
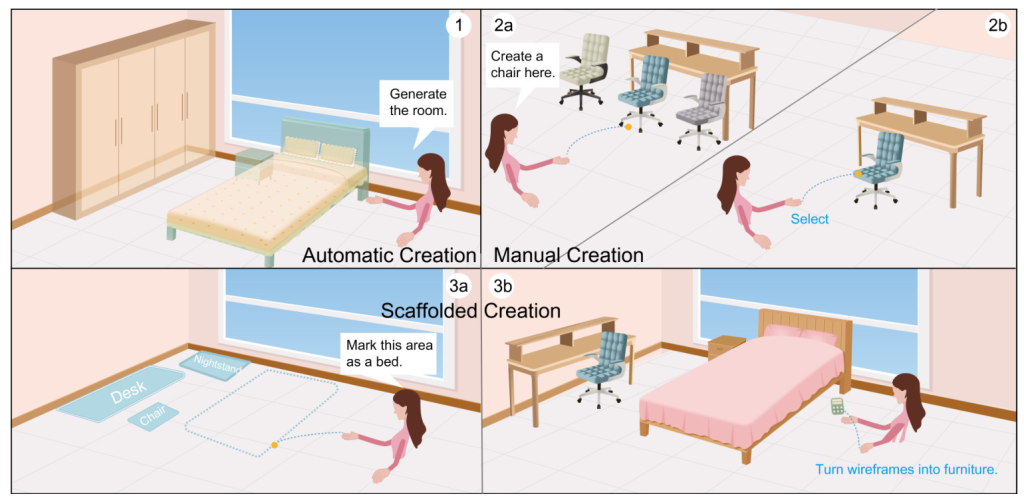
VRCopilot is a mixed-initiative immersive authoring system that enables users to co-create 3D layouts with pre-trained generative models in VR. The system supports three ways of human-AI co-creation: manual creation, automatic creation, and scaffolded creation. Users can manually place objects, request suggestions from the generative model, or create wireframes as intermediate representations to guide the layout generation process.
Scope
VRCopilot is designed for interior design tasks, allowing users to place pre-made 3D furniture models in a virtual apartment. The system includes a large dataset of furniture objects and textures, enabling realistic and diverse design possibilities.
Immersive Authoring Features
VRCopilot offers several immersive authoring features, including importing models from a catalog menu, exploring multiple design alternatives, and using multimodal specification to create individual objects. The system also supports creating wireframes as intermediate representations to scaffold the design process.
Generative Model Integration
VRCopilot integrates the ATISS generative model for indoor scene synthesis, allowing users to generate full-room layouts or suggest individual furniture items. The model is versatile for user inputs and can adapt to various room sizes and shapes.
Multimodal Specification
Users can use speech and simultaneous pointing to specify their creation needs, increasing the naturalness and utility of language description in immersive environments. The system processes natural language voice commands and categorizes them into several possible intents, such as object generation, scene completion, and wireframe generation.
Intermediate Representation
Wireframes are used as intermediate representations for the generated outcomes, allowing users to co-create with the generative model in a more transparent and controllable way. Users can draw wireframes, specify their types, and convert between intermediate representations and 3D layouts.
Experimental Design
User Study 1
The first user study aimed to compare immersive authoring with and without AI. Participants were asked to design an empty apartment under two conditions: using conventional interfaces and using generative AI models. The study sought to understand the challenges and benefits of co-creating with AI in VR.
Participants
Fourteen participants with prior VR experience were recruited from a university. They were compensated for their time.
Procedure
Participants were given a tutorial of the system and then asked to design an apartment under two conditions. Each condition took about 15 minutes to complete. After both conditions, a retrospective interview was conducted.
Analysis
Thematic analysis of interview data and an evaluation workshop with a design expert were conducted to assess the creation results.
User Study 2
The second user study compared three conditions: manual creation, scaffolded creation, and automatic creation. The study aimed to compare user perceived effort, creativity, and agency.
Participants
Fifteen participants with prior VR experience were recruited. They were compensated for their time.
Procedure
Participants experienced all three conditions during the study, designing a bedroom in VR under each condition. They were asked to come up with three design solutions for the same room within 15 minutes.
Measures and Analysis
Post-task surveys measured user perceived effort, creativity, and agency. Thematic analysis of interview data was conducted to understand user perceptions.
Results and Analysis
User Study 1
The first study revealed that generative models provide less user agency but are useful for sparking different ideas. Creation results with AI showed more diverse functionality and color palette but poorer consideration of circulation and daylighting.



User Study 2
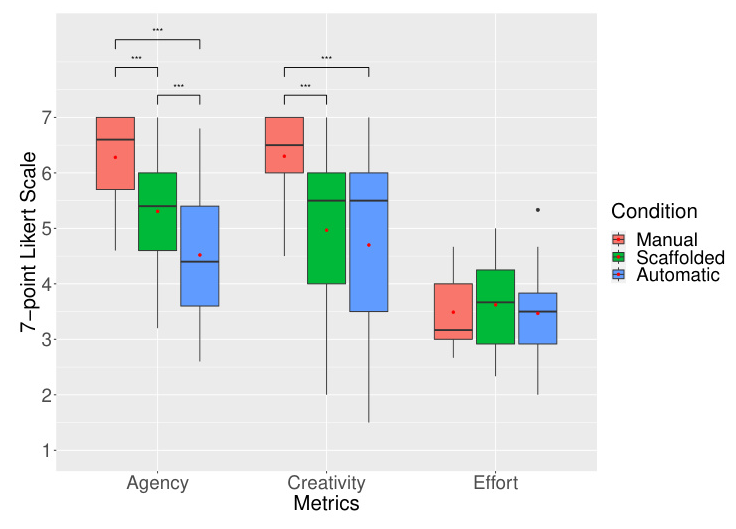
The second study demonstrated that manual creation offers the highest sense of agency and creativity. Scaffolded creation enhances user agency compared to automatic creation, allowing control over furniture size and placement. Users felt the least creative in automatic creation due to fixation on system-generated layouts.
Overall Conclusion
VRCopilot integrates pre-trained generative models into immersive authoring workflows, enabling human-AI co-creation in VR. The system supports manual, automatic, and scaffolded creation, each offering different levels of user agency and creativity. Empirical results from two user studies highlight the potential and challenges of co-creating with generative AI in VR. Manual creation offers the highest sense of agency and creativity, while scaffolded creation provides a balance between control and inspiration. Future research should explore advanced intermediate representations and transparent communication between users and generative AI to enhance the co-creation experience in immersive environments.