Authors:
Sunil Arora、Sahil Arora、John D. Hastings
Paper:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.10351
Introduction
In the digital age, social media has become an integral part of our daily lives, especially for teenagers. While these platforms are designed to enhance social interactions and improve our social lives by facilitating the sharing of personal experiences and life events, they often result in adverse psychological impacts. This study, conducted by Sunil Arora, Sahil Arora, and John D. Hastings, investigates the paradoxical outcomes of social media use among teenagers. The algorithms and structures that underlie social media platforms inadvertently contribute to profound psychological impacts, influencing teenagers in unforeseen ways. This paper issues a call to action for policymakers, platform developers, and educators to prioritize the well-being of teenagers in the digital age and work towards creating secure and safe social media platforms.
Related Work
Psychological Impacts of Social Media on Teens
The widespread use of social media by children and its effect on their mental health has garnered significant attention from the media, researchers, and governments. Several studies emphasize the connection between social media usage and psychological problems among children and teenagers. For instance, a 2023 survey revealed that nearly half of the 1453 surveyed children between the ages of 13 and 17 in the United States used social media apps almost constantly, which doubled compared to 2014-2015. Another survey reported that children spent an average of 8.2 hours daily on social media, and 57% felt they use it too much. These findings highlight the immediate need for action and effective strategies to mitigate social media’s negative psychological impacts on children.
The Rise of Doom Scrolling
Doom scrolling refers to the act of mindlessly scrolling through social media, often out of boredom, habit, or anxiety. This phenomenon was particularly pronounced during the COVID-19 pandemic, as people sought solace in their phones during extended periods of isolation and remote work. Research suggests that prolonged consumption of short-form videos can lead to difficulties in concentration, information retention, and a preference for instant gratification over longer content, ultimately affecting attention span and academic focus.
Research Methodology
Government Regulations
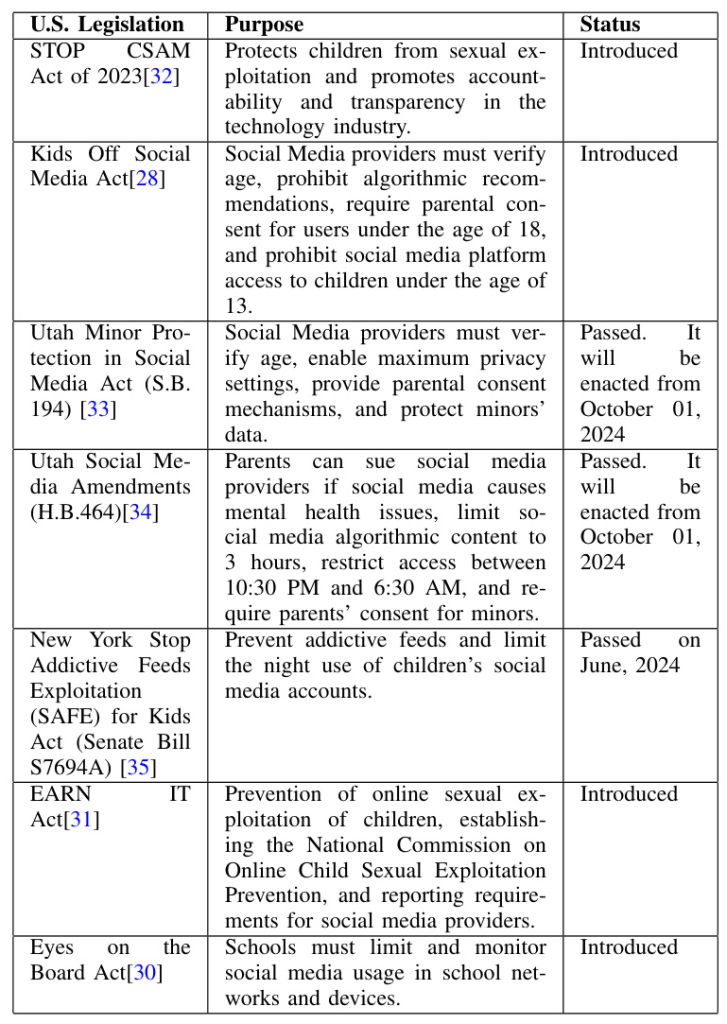
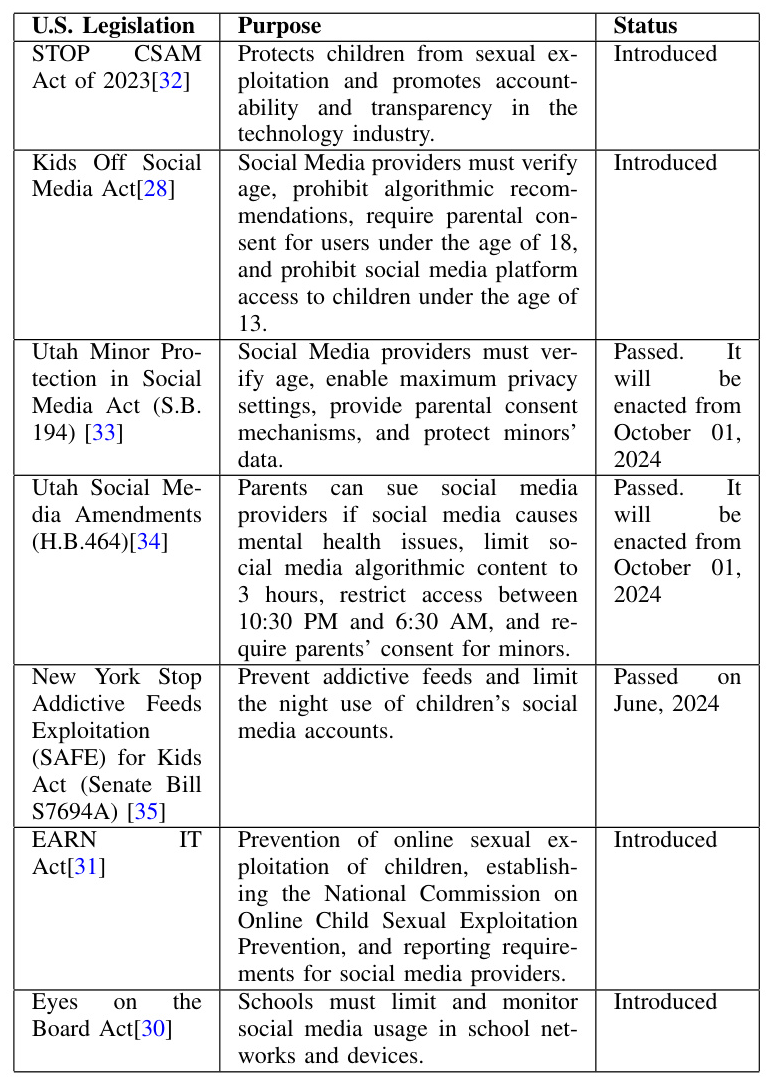
Governments and policymakers have obligations to regulate emerging technologies to protect children from social media harm. Regulations and legislation can be critical in protecting children from social media harm. For instance, the United States has introduced various legislation to protect children from social media harm, such as the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) and the Kids Off Social Media Act. These regulations aim to establish a legal framework and allocate resources to address instances of misconduct.
Industry-led Initiatives
Social media platforms must prioritize effective content moderation to ensure that online discourse remains respectful and safe for all users. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems can assist human content moderators by triaging and prioritizing content based on language or context. Additionally, social media companies must adopt responsible data practices and digital responsibility to protect user data and privacy.
Educational Programs
Educational institutions have a unique opportunity to influence the next generation’s online habits. Digital citizenship encompasses not just the technical skills needed to engage online but also the ethical and responsible behaviors that come with using digital technology. Educational institutions can start by teaching students how to effectively use technology, including basic computer skills, online safety, and digital etiquette.
Experimental Design
Government Regulations
The study examines various government regulations introduced to protect children from social media harm. For instance, the Kids Off Social Media Act prohibits the use of social media by children under 13 and personalized recommendations for those between the ages of 12 and 17. The Earn IT Act of 2023 establishes a National Commission on Online Child Sexual Exploitation Prevention. These regulations aim to establish a legal framework and allocate resources to address instances of misconduct.
Industry-led Initiatives
The study explores industry-led initiatives such as content moderation and responsible data practices. AI algorithms can quickly analyze vast amounts of data to identify potentially problematic content, such as hate speech, violence, or explicit imagery, reducing the workload for human moderators. Additionally, social media companies must adopt responsible data practices to protect user data and privacy.
Educational Programs
The study examines the role of educational programs in shaping responsible digital behavior. Educational institutions can incorporate digital literacy into existing subjects, including health education, social studies, and language arts. Schools can employ role-playing exercises that present hypothetical situations, allowing students to practice responding effectively to online conflicts or encountering inappropriate content.
Results and Analysis
Government Regulations
The study found that government regulations play a critical role in protecting children from social media harm. For instance, the Kids Off Social Media Act and the Earn IT Act of 2023 aim to establish a legal framework and allocate resources to address instances of misconduct. These regulations help increase transparency and establish data protection measures.
Industry-led Initiatives
The study found that industry-led initiatives such as content moderation and responsible data practices are essential in protecting users from harmful content. AI algorithms can assist human content moderators by triaging and prioritizing content based on language or context. Additionally, responsible data practices help protect user data and privacy.
Educational Programs
The study found that educational programs play a crucial role in shaping responsible digital behavior. Educational institutions can incorporate digital literacy into existing subjects and employ role-playing exercises to help students develop essential skills in managing digital interactions and making responsible choices.
Overall Conclusion
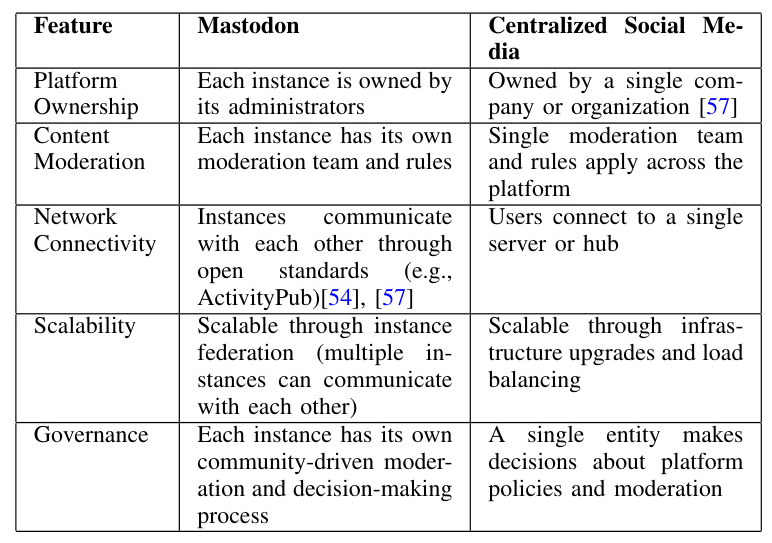
This paper calls for action from the government, social media providers, and educators to work collaboratively to protect our young generation and solve social media’s psychological impact. Government legislation plays a critical role in establishing the regulatory framework to establish safety rules for social media providers to protect children online. The social media industry must collaborate and take initiatives such as enhanced content moderation and algorithmic adjustments. Furthermore, exploring alternative platforms, such as Mastodon, offers a glimpse into the potential of decentralized social media models that prioritize user control and privacy. In summary, addressing the impact of social media on children demands an integrated approach, combining legislative action, industry responsibility, educational initiatives, and continued innovation in social media platforms.