Authors:
Paper:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.08915
Introduction
Supply Chain Finance (SCF) plays a crucial role in enhancing supply chain competitiveness by optimizing capital flow. The advent of Blockchain technology, with its features of data integrity, authenticity, privacy, and information sharing, has the potential to revolutionize SCF. This survey aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Blockchain-based SCF, summarizing current applications and proposing future research directions.
Supply Chain Finance
Supply Chain Finance Overview
Global trade globalization has complicated supply chain mechanisms, putting pressure on capital flow. Large enterprises often dominate supply chains, causing financing difficulties for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). SCF aims to alleviate these issues by optimizing capital flow management and reducing financing risks and costs.
What is Supply Chain Finance?
SCF integrates financial flows into the physical supply chain to improve management. It provides comprehensive financial products and services to upstream and downstream enterprises based on core customers. SCF includes supplier financing and distributor financing, with specific programs like accounts receivable financing, inventory financing, prepayment financing, and strategic relationship financing.
Research Direction of Supply Chain Finance
Research on SCF can be divided into management science and computer science perspectives. Management science focuses on financial and supply chain attributes, while computer science leverages advanced technologies like big data, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and Blockchain to optimize SCF operations.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain Overview
Blockchain technology, first introduced with Bitcoin by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008, has gained significant attention in various fields, including finance, supply chain, and healthcare. Blockchain’s decentralized, tamper-proof, and cryptographic features make it suitable for SCF applications.
What is Blockchain?
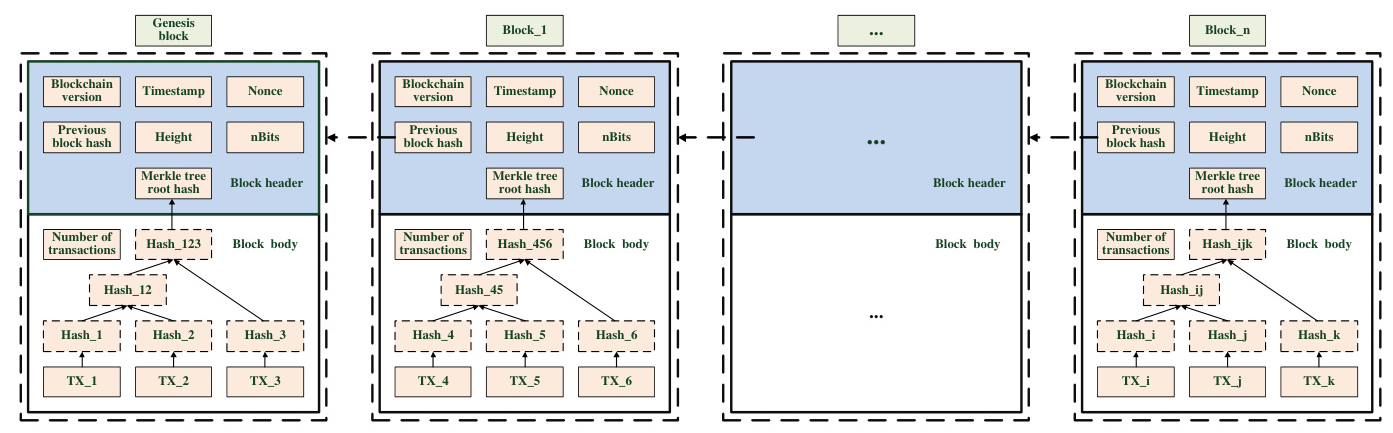
Blockchain is a data structure that stores historical transaction data in a decentralized, transparent, and secure manner. It consists of blocks linked in chronological order, forming a chain. Each block contains a block header and block body, with the header including metadata and the body containing transaction records.
Blockchain Structure and Core Technology
Blockchain combines several technologies, including distributed storage, encryption, peer-to-peer networking, incentive mechanisms, and smart contracts. These technologies ensure data integrity, security, and consensus among network participants.
Research Directions of Blockchain Essential Technology
Storage
Blockchain’s distributed storage ensures data transparency but poses storage challenges. Research focuses on reducing storage consumption and expanding off-chain storage space.
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer networks support Blockchain’s decentralization. Research aims to improve message propagation latency and enhance security and trust.
Encryption
Encryption ensures data security and privacy in Blockchain. Research includes homomorphic encryption, zero-knowledge proofs, and attribute-based encryption.
Consensus Mechanism
Consensus mechanisms ensure data consistency in Blockchain networks. Research includes permissioned and permissionless consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
Incentive Mechanism
Incentive mechanisms motivate nodes to participate in Blockchain networks. Research includes computation, storage, and transmission incentives.
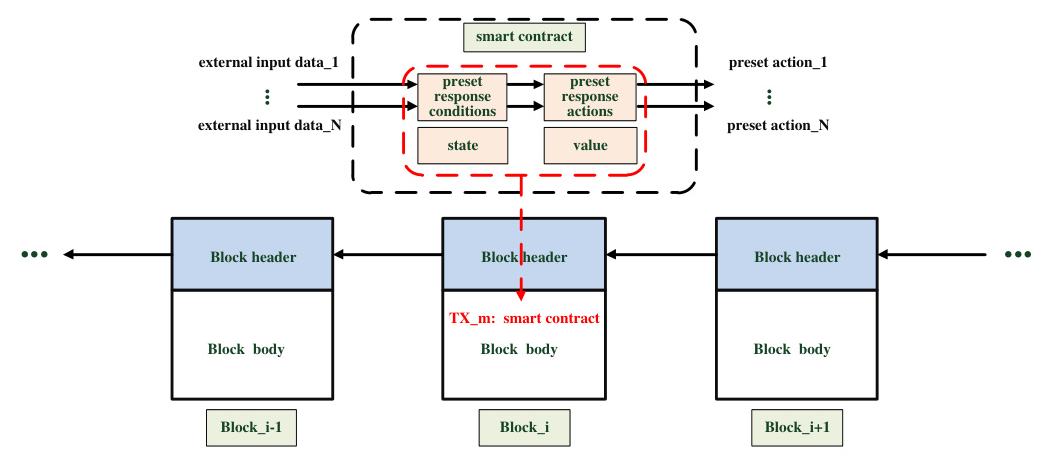
Smart Contract
Smart contracts automate transactions based on predefined conditions. Research focuses on enhancing security, privacy, computation efficiency, and overall performance.
Cross Chain
Cross-chain technology enables interoperability between different Blockchains, addressing information silos and enhancing data sharing.
Applications on the Combination of Blockchain with Other Computer Technologies
Blockchain + Data Analysis
Blockchain’s unique data characteristics make it suitable for data mining and analysis, addressing privacy, sharing, and data integrity challenges.
Blockchain + Internet of Things
Blockchain enhances IoT applications by ensuring data integrity, security, and privacy.
Blockchain + Artificial Intelligence
Combining Blockchain with AI leverages Blockchain’s data storage capabilities and AI’s data processing and decision-making abilities.
Applying Blockchain to Supply Chain Finance
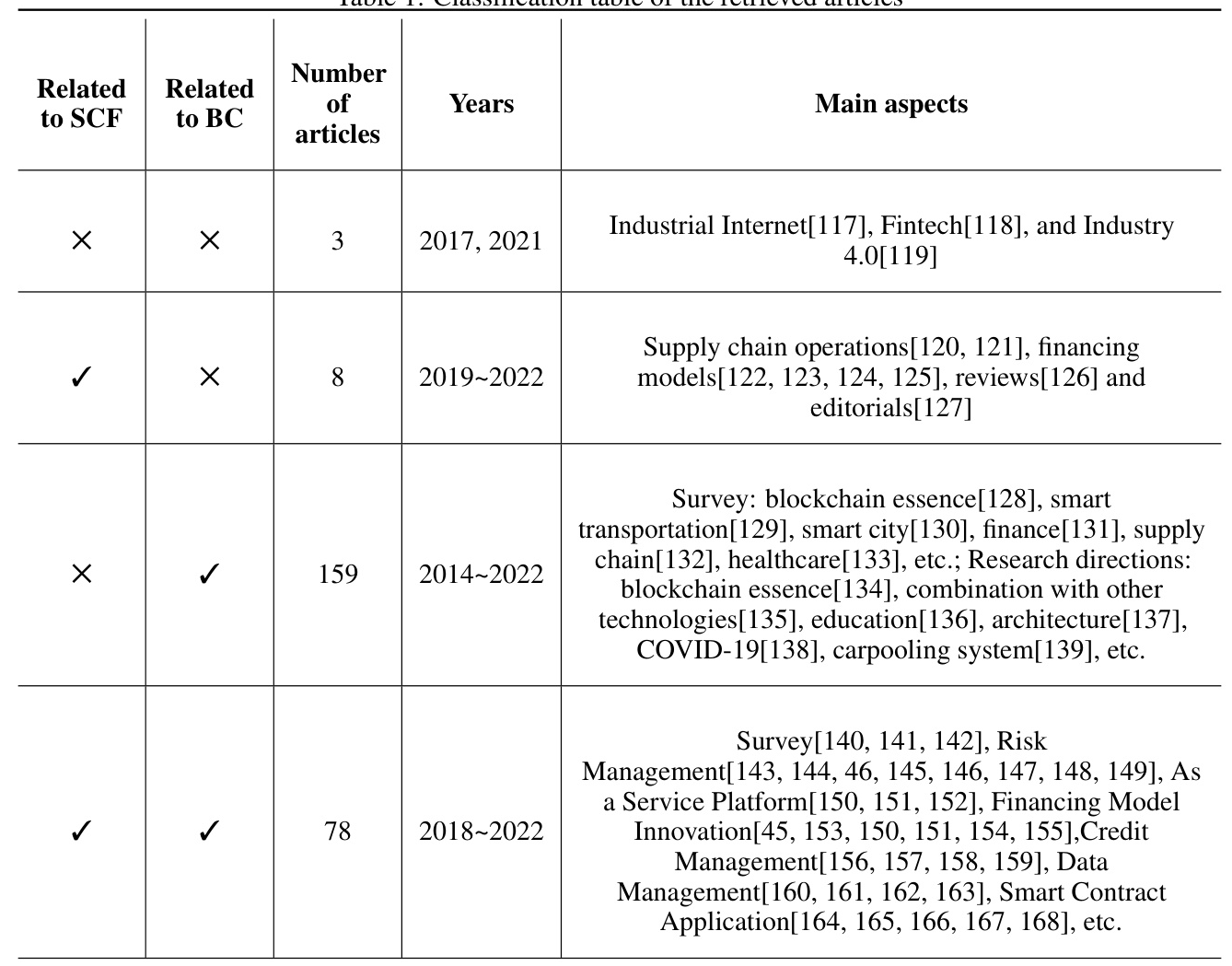
Literature Research Content and Trend Analysis
A comprehensive literature review reveals that Blockchain-based SCF research focuses on risk management, service platforms, financing models, credit management, data management, and smart contract applications.
Application Hot-topics
Risk Management
Blockchain enhances risk management by providing trusted data storage, enabling Blockchain computing, and considering Blockchain as a risk factor.
As a Service Platform
Blockchain serves as a trustworthy platform for SCF, facilitating information sharing and business operations among supply chain members.
Financing Model Innovation
Blockchain transforms SCF business models, ensuring information symmetry and controllability in financing operations.
Credit Management
Blockchain improves credit assessment, disassembly, transmission, and risk control in SCF.
Data Management
Blockchain ensures data privacy, tamper-proofing, sharing, and storage in SCF.
Smart Contract Application
Smart contracts automate SCF operations, reducing human errors and enhancing efficiency.
Future Directions on Blockchain-based Supply Chain Finance
Data Management for Supply Chain Finance
Blockchain-based Supply Chain Finance Dataset Construction
Creating publicly available SCF datasets will enhance research and development in Blockchain-based SCF.
Data Privacy Protection
Fine-grained privacy protection mechanisms are essential for secure and trustworthy SCF operations.
A Comprehensive Blockchain-based Platform for Supply Chain Finance
Developing a comprehensive Blockchain-based service platform will facilitate SCF applications, integrating various Blockchain modules and ensuring data security.
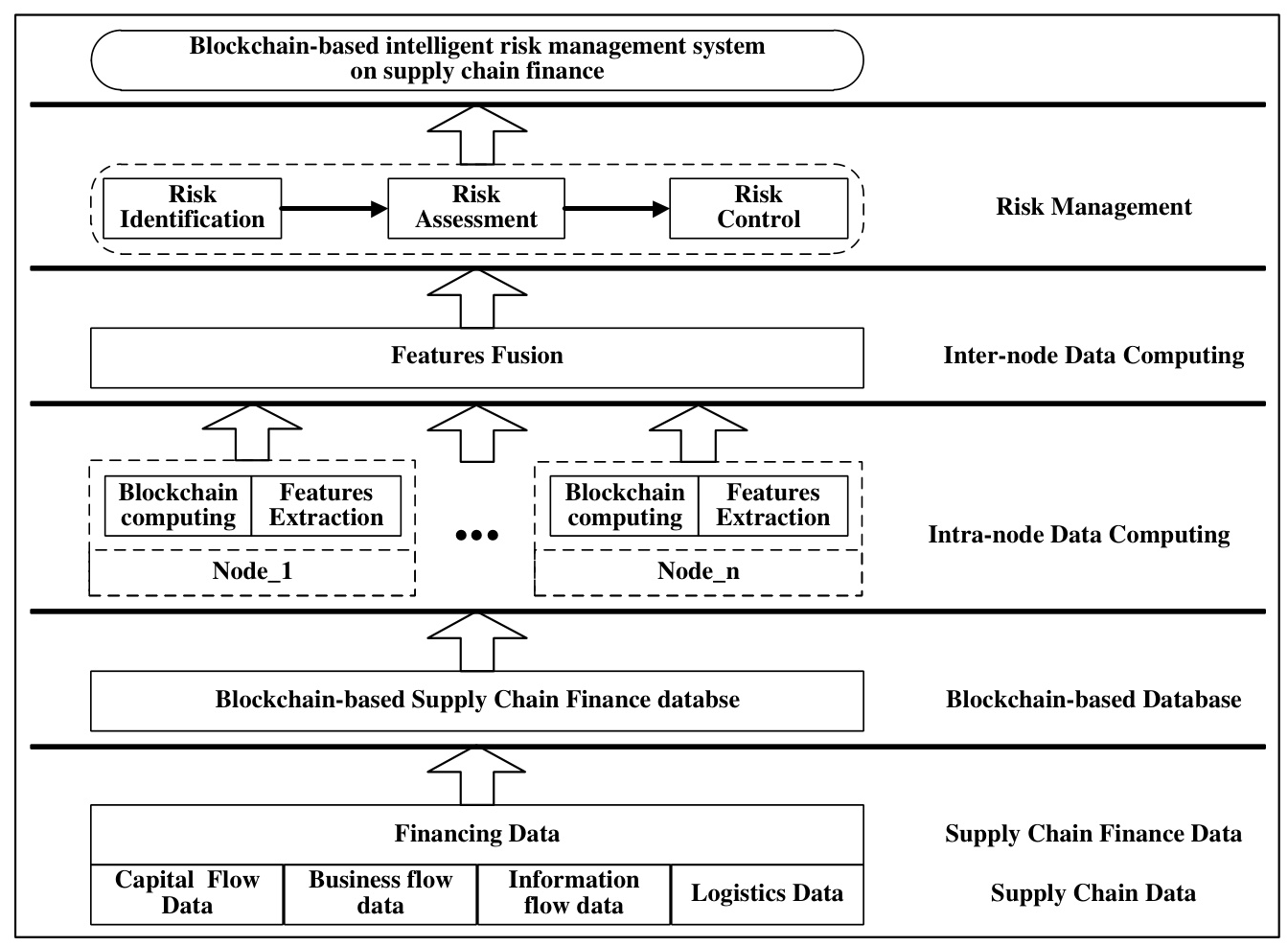
Intelligent Risk Management for Supply Chain Finance
Combining Blockchain with AI and data mining will enable intelligent risk management, enhancing decision-making and risk control.
Visualization of Blockchain-based Supply Chain Finance
Visualization technologies will help analyze and monitor SCF data, enhancing risk detection and business operations.
Cross-chain Research on Blockchain-based Supply Chain Finance
Cross-chain technology will enable comprehensive data access and verification, improving SCF risk assessment and business processing.
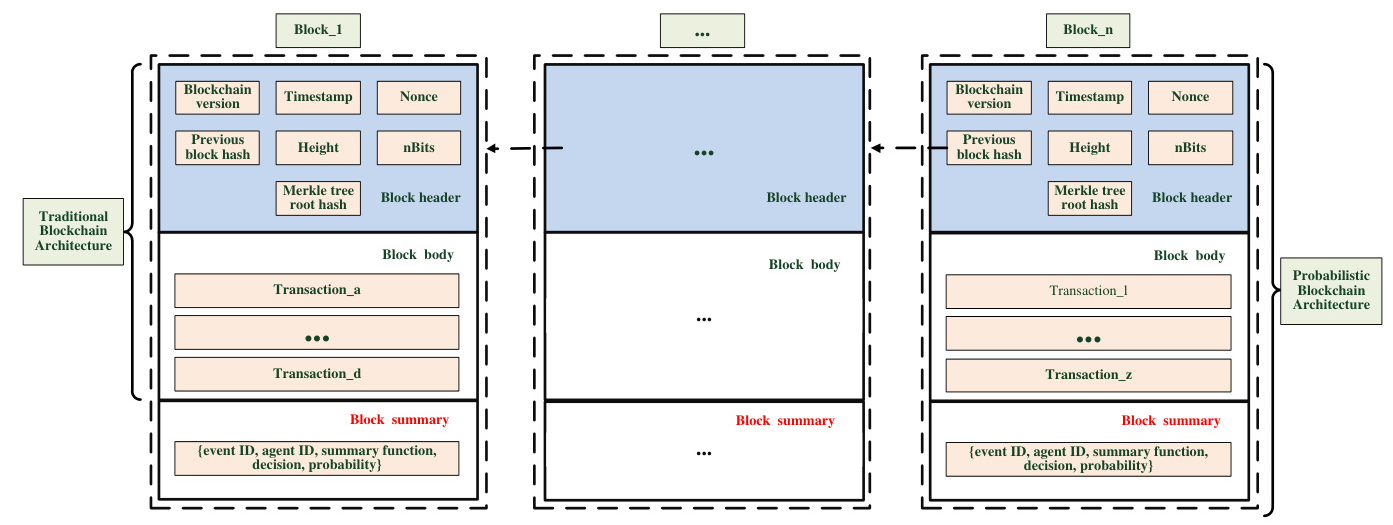
Blockchain Computing
Blockchain computing will extend Blockchain’s capabilities, enabling probabilistic event storage and advanced data processing.
Extending Smart Contract for Blockchain-based Supply Chain Finance
Expanding smart contract applications will enhance SCF automation and intelligence, integrating advanced technologies for improved performance.
Other Promising Research Directions on Blockchain-based Supply Chain Finance
Exploring government auditing, federated computing, Blockchain machine construction, and integrating emerging technologies like metaverse and AI will further advance Blockchain-based SCF.
Conclusions
Blockchain technology significantly enhances SCF by improving financing systems, promoting intelligence and automation, and optimizing costs. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of Blockchain-based SCF applications and proposes future research directions, emphasizing the need for further exploration and innovation in this promising field.

