Authors:
Akriti Verma、Shama Islam、Valeh Moghaddam、Adnan Anwar、Sharon Horwood
Paper:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.07704
Introduction
In today’s digital age, social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Reddit, and Instagram have become integral to our daily lives. These platforms serve as avenues for sharing emotions and seeking emotional support, thus playing a crucial role in managing people’s emotions. However, these platforms are not specifically designed for emotion regulation, which limits their effectiveness. This paper proposes an innovative approach to enhance Interpersonal Emotion Regulation (IER) on online platforms through content recommendation. The goal is to empower users to regulate their emotions by recommending media content that aligns with IER strategies, particularly empathic responding.
Literature Review
Emotion Regulation Online
Emotion regulation is a critical aspect of human psychology, influencing mental health and interpersonal relationships. Digital media platforms offer opportunities for individuals to seek and receive emotional support, share experiences, and access resources that aid in emotion regulation. Recent research has explored how individuals use various social media applications to regulate their emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. These studies have highlighted the role of social media in alleviating homesickness, the impact of multitasking and passive scrolling habits, and the effectiveness of biofeedback and haptic interactions in providing real-time support.
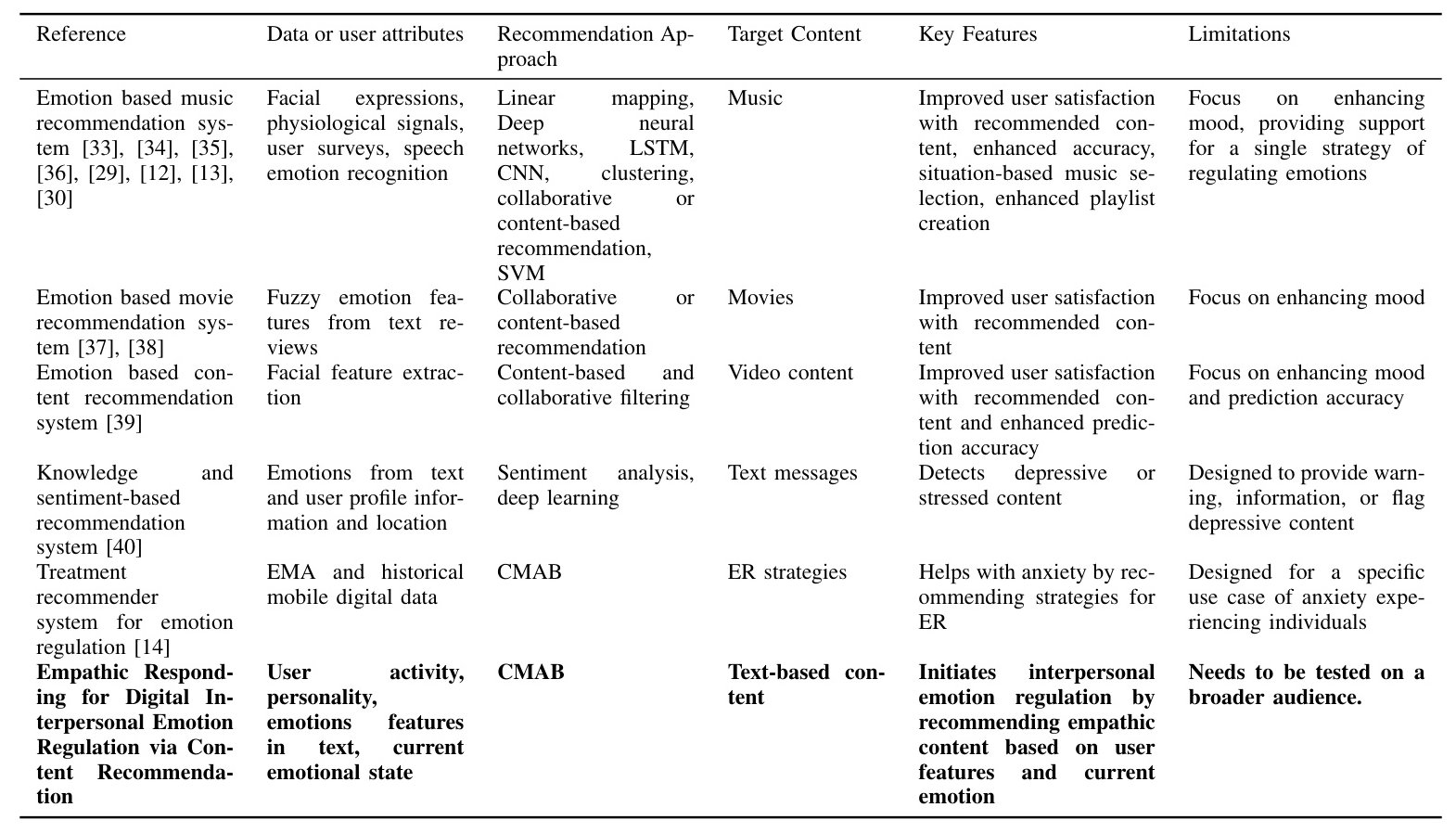
Emotion-Based Content Recommendation
Empathy, the ability to understand and share others’ emotions, is vital for effective communication and emotional regulation. Incorporating empathic content into digital platforms has shown positive results in boosting emotional well-being and fostering connections between individuals. Recent literature has seen the development of several emotion-based recommendation systems aimed at improving user satisfaction and accuracy in content recommendations across different domains. However, most existing systems focus on enhancing mood rather than actively helping users regulate their emotions.
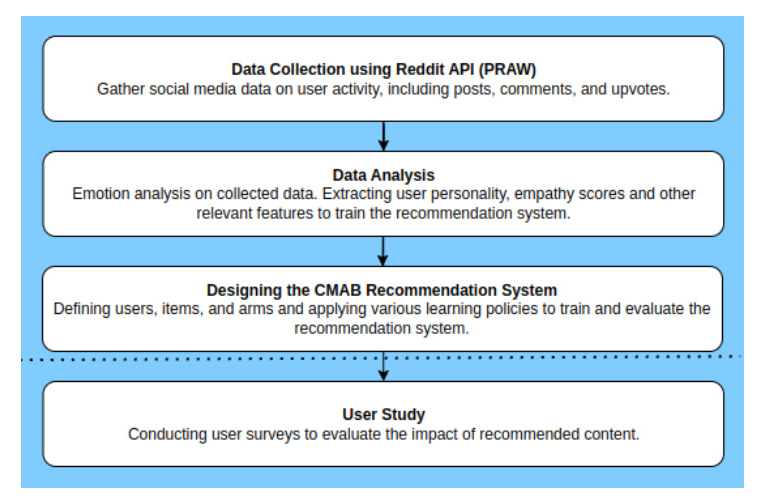
Proposed Framework
The proposed framework designs empathic recommendations on social media by utilizing two key components: a quantitative analysis of Reddit user behavior and a user study to evaluate the impact of recommended content. The framework involves collecting text-based social media data, analyzing user personality and empathy scores, and training a Contextual Multi-Armed Bandit (CMAB) based recommendation system.
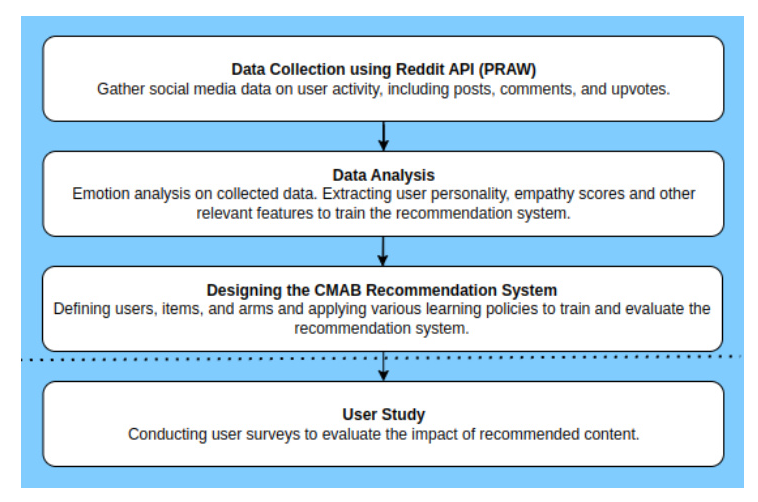
Data Collection and Preprocessing
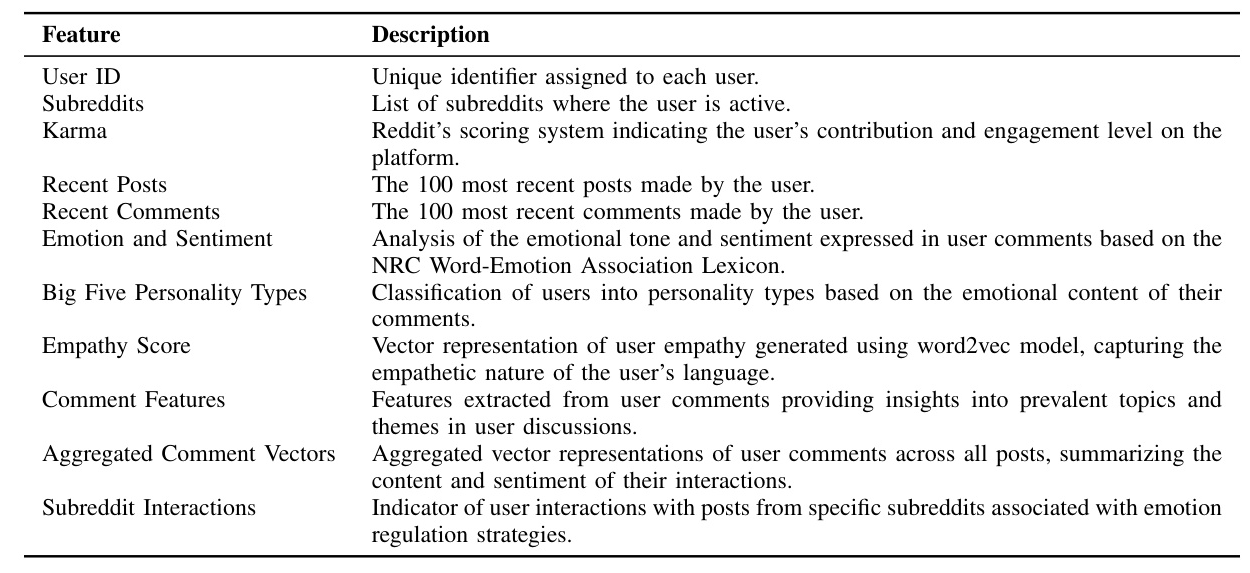
Data was collected from Reddit, focusing on text-based posts and interactions. The dataset comprised 375,350 rows of user activity and statistics. The data was cleaned and preprocessed to remove extraneous characters, links, and special symbols. User features such as emotion and sentiment, Big Five personality types, empathy scores, and comment features were extracted for analysis.
Training
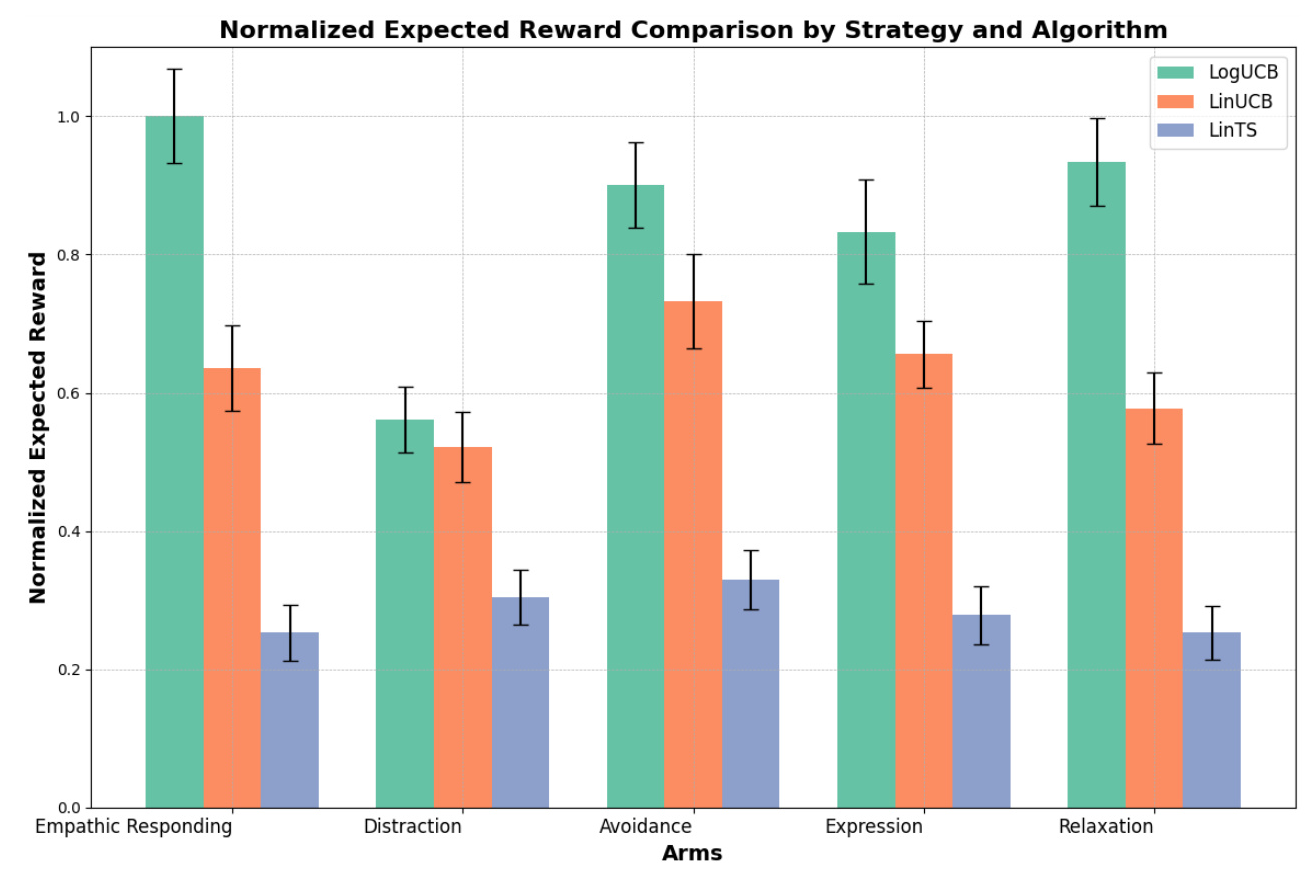
The CMAB algorithm was used to optimize rewards in dynamic environments by balancing exploration and exploitation. Three prominent contextual bandit algorithms were compared: Linear Thompson Sampling (LinTS), Linear Upper Confidence Bound (LinUCB), and Logistic Upper Confidence Bound (LogUCB). The LogUCB policy outperformed the other evaluated policies for four out of five arms of the CMAB.
Evaluation
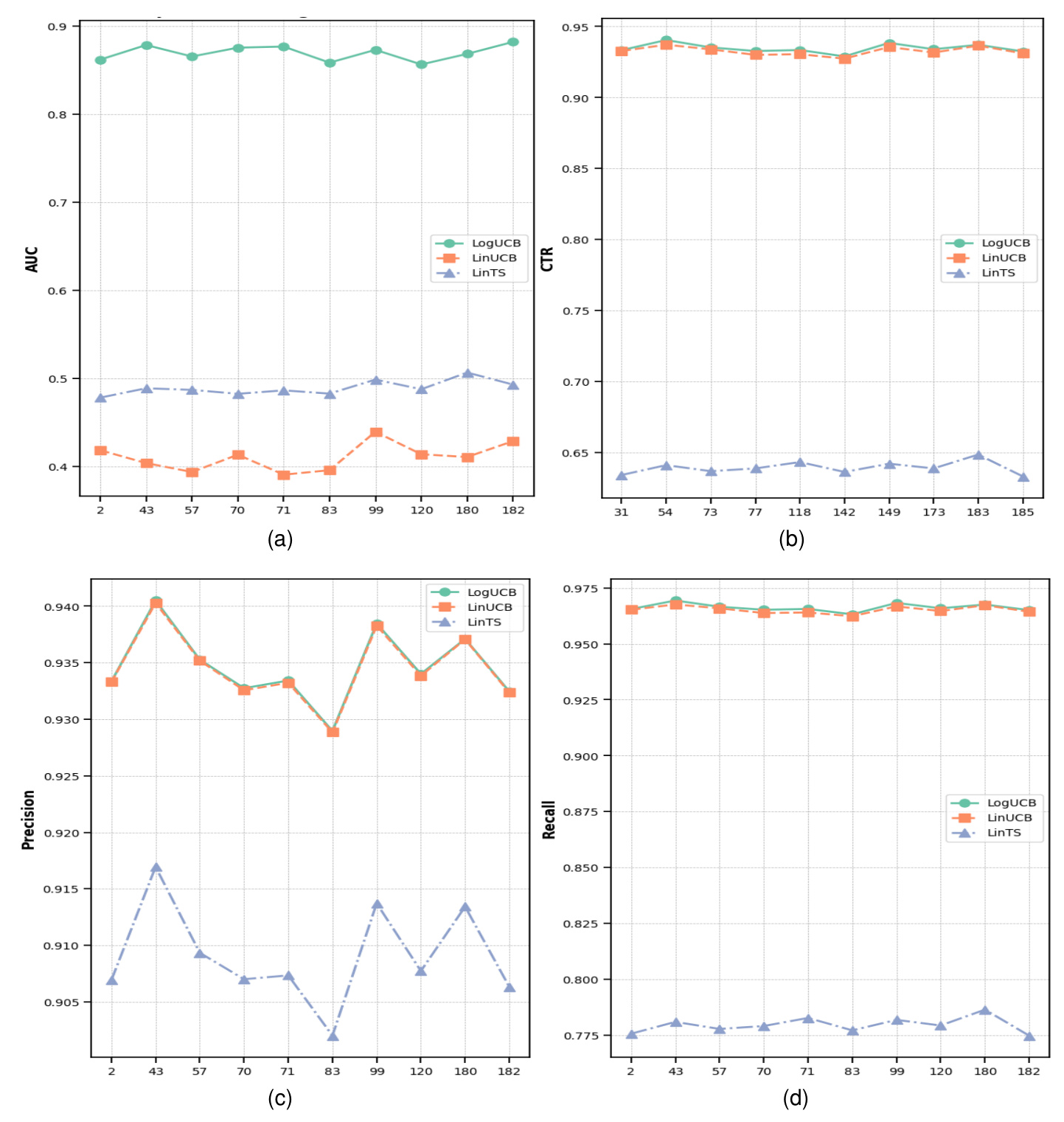
The performance of the recommendation algorithms was evaluated using metrics such as Area Under the Curve (AUC), Click-Through Rate (CTR), Precision, and Recall. LogUCB consistently demonstrated strong performance across all metrics, making it the best performer among the three policies.

User Survey
A user study was conducted to assess how users responded to the empathetic content generated by the CMAB recommender. Participants completed a brief questionnaire three times per day for seven consecutive days. The survey aimed to gain insights into users’ emotional states, preferences for emotional regulation strategies, and interactions with digital platforms.
Results and Discussion
The results revealed that empathic responding was a preferred strategy for managing four of the six emotions, with participants showing a tendency to engage in empathetic responses, especially during moments of heightened emotional intensity. Strategies such as “Empathic Responding” and “Relaxation” consistently demonstrated higher intensity levels across most emotions. Distraction and avoidance showed varying degrees of effectiveness depending on the emotional context.
Limitations
Several limitations warrant consideration. The study focused on a subset of emotion regulation strategies, which may not provide a complete understanding of emotion regulation dynamics in online environments. The user study involved a relatively small sample size, which may constrain the generalization of the results. Additionally, the study primarily relied on text-based social media data from Reddit, which may not fully capture the dynamics of emotion regulation across various digital platforms.
Conclusion
This study introduced a novel recommendation system designed to promote empathic responding strategies and enhance IER on digital platforms. The proposed system demonstrated promising results, with users consistently preferring empathic recommendations over other emotion regulation strategies. This research lays the groundwork for emotion regulation in digital media, guiding the development of more supportive online environments.
By integrating effective emotion regulation strategies, digital applications can promote positive interactions and improve user well-being, making online platforms more supportive and empathetic spaces.